October
25, 2007
Reservoir
Levels in the Southwest
(The
data in this table are from Arizona Game and Fish)
Alamo
Reservoir:
Max. Elevation
(ft): 1,235 Current Elevation (ft): 1,112
Max. Surface
(acres): 13,300 Current Surface (acres): 3,196
Feet Below
Max.: -123 Percent Full: 12%
Apache
Lake: (Horse Mesa)
Max. Elevation
(ft): 1,914 Current Elevation (ft): 1,909
Max. Surface
(acres): 2,656 Current Surface (acres): 2,580
Feet Below
Max.: -5 Percent Full: 95%
Bartlett:
Max. Elevation
(ft): 1,798 Current Elevation (ft): 1,756
Max. Surface
(acres): 2,815 Current Surface (acres): 1,692
Feet Below
Max.: -42 Percent Full: 48%
Canyon
Lake: (Mormon Flat)
Max. Elevation
(ft): 1,660 Current Elevation (ft): 1,605
Max. Surface
(acres): 947 Current Surface (acres): 517
Feet Below
Max.: -55 Percent Full: 29%
Lake
Havasu:
Max. Elevation
(ft): 450 Current Elevation (ft) : 447
Max. Surface
(acres): 20,400 Current Surface (acres): 19,100
Feet Below
Max.: -3 Percent Full: 91%
Lake
Havasu, unlike Lake Powell and Lake Mead is not allowed to
substantially
change its storage. This is the result of it being a feeder lake
into the
Los Angeles aqueduct system
Horseshoe
Lake:
Max. Elevation
(ft): 2,026 Current Elevation (ft): 1,953
Max. Surface
(acres): 2,812 Current Surface (acres): 548
Feet Below
Max.: -73 Percent Full: 3%
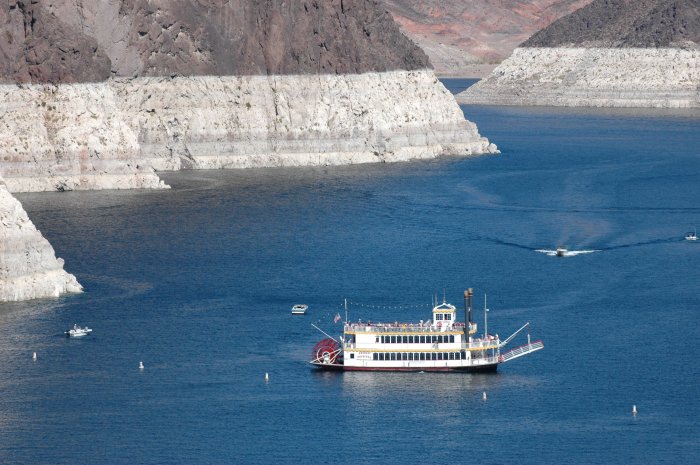
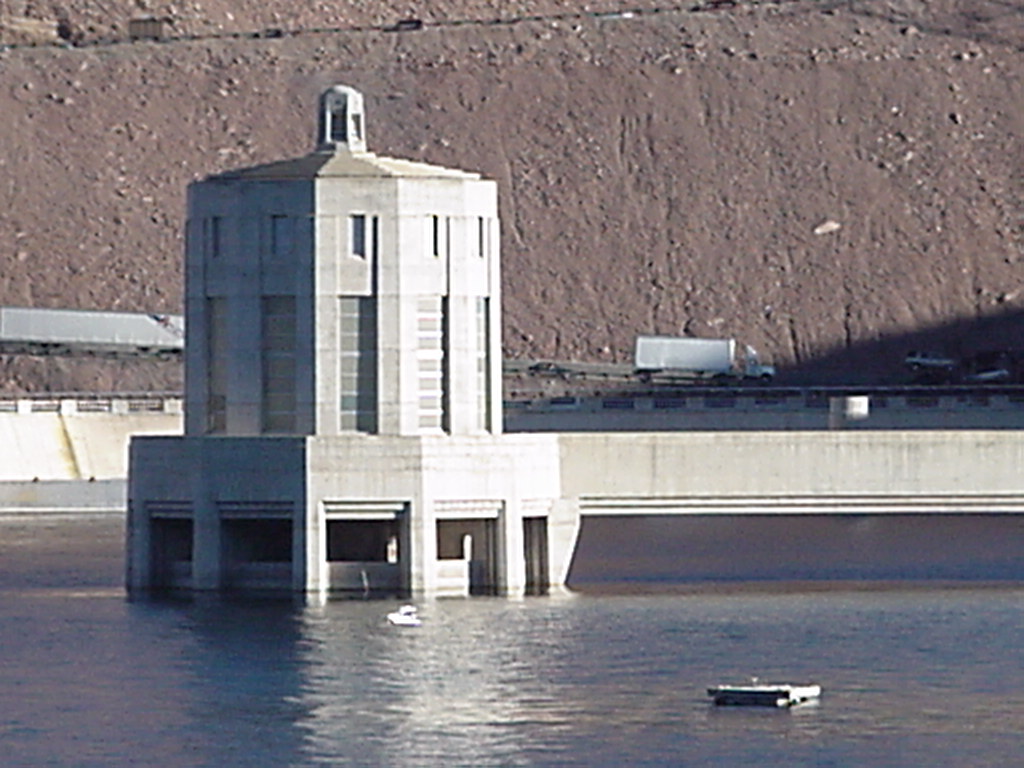
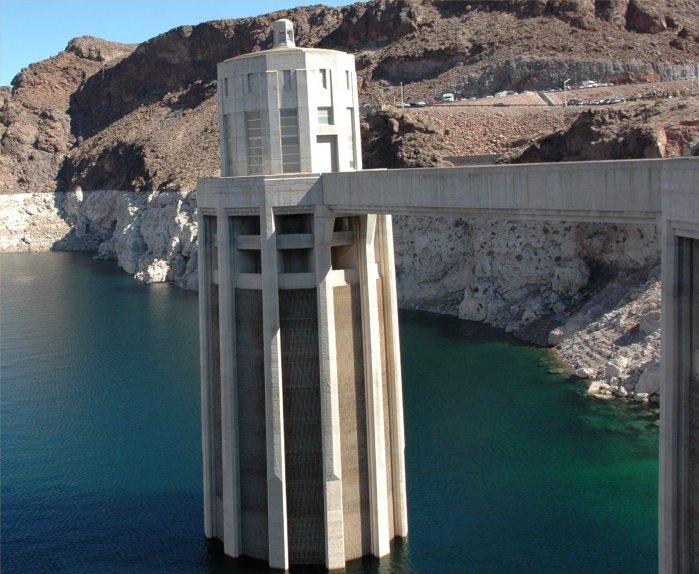
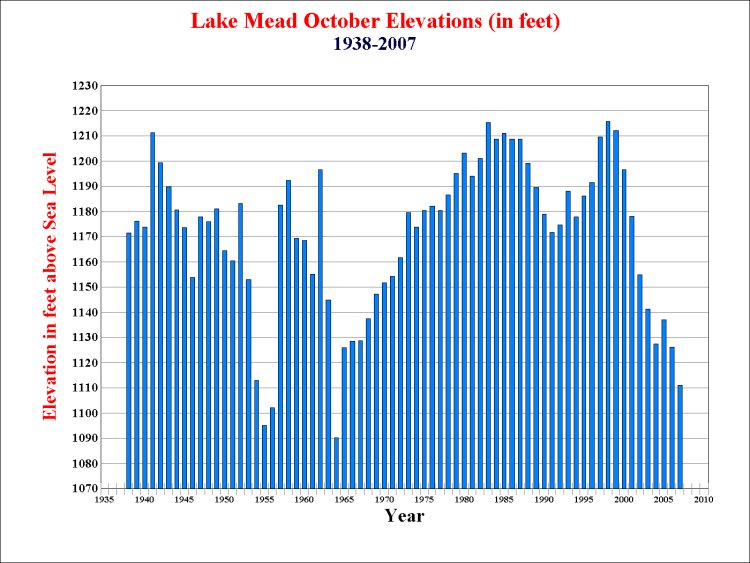
Lake
Mead:
Max. Elevation
(ft): 1,229 Current Elevation (ft): 1,111
Max. Surface
(acres): 162,700 Current Surface (acres): 93,900
Feet Below
Max.: -118 Percent Full: 46%*
* Percent
Full calculations does not include the flood control volume adjustment
Lake
Mohave:
Max. Elevation
(ft): 647 Current Elevation (ft): 634
Max. Surface
(acres): 28,800 Current Surface (acres): 25,700
Feet Below
Max.: -13 Percent Full: 81%
Lake
Pleasant: (Waddell Dam)
Max. Elevation
(ft): 1,702 Current Elevation (ft): 1,644
Max. Surface
(acres): 9,957 Current Surface (acres): 6,268
Feet Below
Max.: -58 Percent Full: 46%
Lake
Powell:
Max. Elevation
(ft): 3,700 Current Elevation (ft): 3,601
Max. Surface
(acres): 160,800 Current Surface (acres): 95,900
Feet Below
Max.: -99 Percent Full: 49%
Roosevelt
Lake:
Max. Elevation
(ft): 2,151 Current Elevation (ft): 2,099
Max. Surface
(acres): 21,493 Current Surface (acres): 13,455
Feet Below
Max.: -52 Percent Full: 46%
San
Carlos:
Max. Elevation
(ft): 2,525 Current Elevation (ft): 2,441
Max. Surface
(acres): 19,985 Current Surface (acres): 5,539
Feet Below
Max.: -84 Percent Full: 12%